AI is undoubtedly the biggest buzzword these days. Since the release of ChatGPT in 2022, the frenzy has been growing. The COMPUTEX 2024 show headlined the theme “Connecting AI,” with NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang’s keynote taking center stage. Adding to the excitement, Apple Intelligence was launched recently. Much of the anticipation for what AI can do for humanity seems to be materializing in ways that will continue to change how we conduct our day-to-day lives.
In McKinsey’s latest Global Survey on AI (May 2024), 72% of organizations have adopted AI in some form or another. This marks a notable rise versus an adoption rate that hovered at just over 50% in the previous five years, no doubt fueled by surging interest, particularly in generative AI.
Increasingly more AI applications are coming to market with the aim of being used in everyday consumers’ lives. We’ll outline some of the more interesting applications that we noticed in business, health, food, and entertainment.
Business — Smart Video Conferencing Solutions
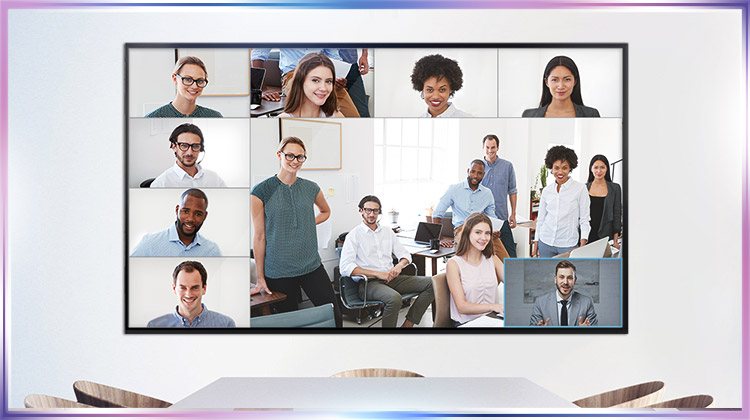

Meeting technology has come a long way. AI is often used in business conferencing settings, incorporated into cameras and conferencing software. For instance, AVer’s Smart Composition enhances USB PTZ camera capabilities with AI that helps detect participants’ faces and displays them in equal proportions, facilitating an efficient, natural communication process. By ensuring that the face of each participant is visible to everyone, participants can communicate more freely and clearly.
Beyond online meeting requirements, more businesses, like Aira, are creating AI facial recognition solutions for surveillance and workforce management systems. Placed at an entrance, the AI systems are applied to contactless access control, capable of recognizing employees, maintaining attendance records, registering visitor information, and identifying VIPs and blacklisted individuals. Some systems even include fever screening to maintain healthier work environments.
Health — Medical Camera and AIoT Solutions for Personal Care
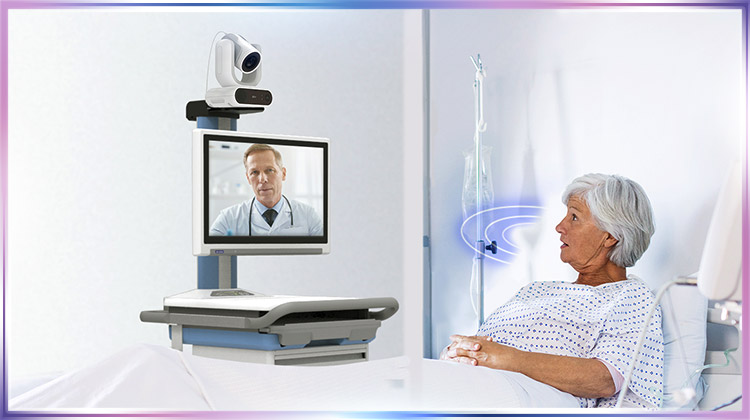
AI is transforming telehealth camera capabilities by enhancing the effectiveness of telehealth consultations, improving patient surveillance, streamlining operational processes, and broadening the reach of healthcare services. The effectiveness of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic was, in many cases, comparable to in-person care in various clinical areas and outcomes.
For patient-doctor communication, AI applications exist in medical grade cameras to improve doctor-patient communication in telehealth. As acoustics during a telemedicine session can affect the communication process and sometimes even the diagnosis, AVer uses AI in acoustics to reduce unwanted noise and provide clearer audio to improve communication. These AVer telehealth cameras have high-quality audio and high-resolution lenses for the best presentation of details, so doctors can make better clinical decisions for their patients.
Because of the pandemic, demand for automated disinfection solutions in healthcare and public areas to reduce the risk of infection has grown tremendously. Artificial Intelligence of Things (AIoT) companies like MSI have developed disinfection robots for indoor areas that incorporate AI for site surveys, navigation route planning, human detection, and air and surface UV sterilization. This easily keeps indoors clean and safe from viruses and bacteria, especially in higher-risk venues such as hospitals and laboratories.
Food — From Coffee Sorting to Order Management and Food Processing
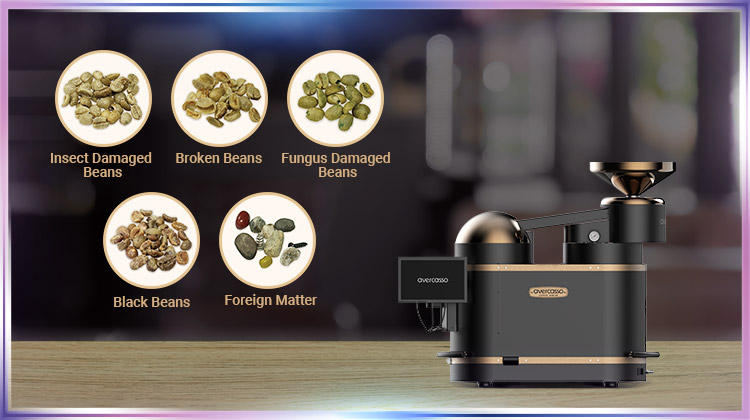

Sorting food in the preliminary stages of food production is a prime candidate for the application of AI. When raw materials such as coffee beans are obtained, they often need to undergo a selection process to eliminate beans with deficiencies like discoloration, fermentation, mold, and insect damage. Manual hand sorting by workers involves repetitive work for long hours, which is time-consuming and mentally draining. The avercasso® AI coffee bean sorter, for example, takes the coffee sorting process to the next level. By sorting beans into good and defective batches automatically and accurately, it alleviates the painful process of green bean sorting before the beans are roasted. This type of coffee roasting process technology can be leveraged in other food processes, such as factory quality control and other selection processes.
AI, of course, can do much more than sort coffee beans. In restaurants, food ordering and preparation can be automated through AI, with companies like LaFresh creating kiosks equipped with multilanguage AI voice recognition so customers can speak to place orders. For store management, AI can calculate and forecast food usage and, in turn, reduce food and financial waste.
AI can create and optimize complex processes in any food industry application, assisting in sifting through large amounts of data efficiently and automatically. For example, AI helps Unilever, the consumer products conglomerate, asses shelf life, texture, and taste while forecasting the product’s performance on factory production lines.
Entertainment — Broadcasting and Gaming Like Never Before
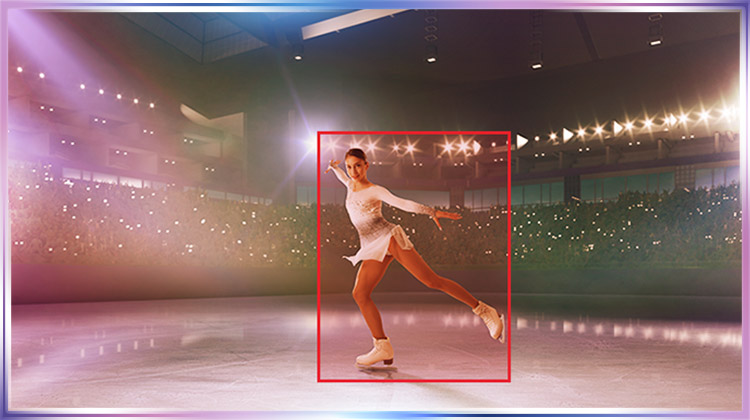

For live performances, AI camera tracking technologies can follow specific performers to automatically stream and film performances without manual operation. These live streaming camera capabilities offer different tracking modes, automatically adjusting the framing to catch the best angles of the performance.
On video platforms like YouTube, AI is an indispensable tool in helping to flag or remove inappropriate content, add video effects, make viewing recommendations, and potentially even make insightful predictions of human behavior. Though not perfect, AI undoubtedly processes a significant amount of video content quicker than a human does, speeding up the identification of videos that do not comply with platform standards. This is especially important in distance learning or classroom broadcasting scenarios.
In gaming, generative AI can now be used to assist game developers in building NPC characters, creating convincing backstories, and animating the characters. This opens a whole new world to gamers, as the games are no longer strictly limited to what the developers' script says, allowing games to unfold with many more possibilities. Meanwhile, NVIDIA’s G-Assist acts as an AI assistant that enriches the gaming experience by helping gamers optimize their game settings, manage their gaming library, and capture and share gameplay highlights.
Unleashing the Potential of AI
We’ve only mentioned a few uses of AI in four select areas, but AI applications are becoming more ubiquitous, streamlining different parts of our lives. Soon, video conferencing hardware could work with AI voice controls to automate camera operations during a virtual meeting or presentation. AI image analysis could be used in telemedicine to support medical examinations, not to mention greater efficiencies in food processing. And utilizing AI to create videos, movies, and games is just a natural fit. With generative AI development growing at an exponential rate, its use could be more extensive, bringing even greater convenience to our lives. With these possibilities in mind, which AI applications are you the most excited about?
References
-
Singla, Alex. “The State of AI in Early 2024: Gen AI Adoption Spikes and Starts to Generate Value.” May 30, 2024.
-
“Boasting Accurate Recognition, Flexible Deployment and Friendly Cost, AIRA's AI Solutions Revolutionize Security Management.” May 22, 2024.
-
Hatef, E., Wilson, R.F., Zhang, A. et al. “Effectiveness of telehealth versus in-person care during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review.” npj Digit. Med. 7, 157 (2024).
-
Doering, Christopher. “How Unilever Is Embracing Artificial Intelligence to Revolutionize Food Development.” May 28, 2024.
-
Marr, Bernard. “The Amazing Ways YouTube Uses Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning.” August 23, 2019.