Patient falls in hospitals and healthcare facilities are a significant concern. Each year, roughly 700,000 to 1 million patient falls occur in U.S. hospitals, resulting in around 250,000 injuries and up to 11,000 deaths. Currently, 24/7 telesitting would improve this situation, but with the nurse shortage, it is more challenging than ever. Patients who are at higher risk of falling require timely intervention, and it is crucial to mitigate these risks and improve patient outcomes with telesitting technology.
In this article, we will explore the common fall detection technologies used in healthcare settings, discuss their benefits, and examine the limitations and challenges associated with their implementation.
Understanding Fall Detection Technologies
Fall detection technologies play a crucial role in enhancing patient safety by providing real-time monitoring and alerts. These innovative solutions come in various forms, each designed to address different aspects of fall prevention and detection. Commonly used solutions include:
- Camera-based Systems: Cameras with AI algorithms that detect falls in real-time, providing continuous monitoring without wearable devices. Ideal for larger areas or multiple patients, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
- Wearable Devices: Smartwatches and necklaces with sensors that detect falls and send alerts to healthcare providers. These devices offer continuous monitoring and are comfortable for patients.
- Pressure Sensors: Devices under mattresses or integrated into bed sensors to monitor movements and detect falls, adding safety for bedridden patients.
- Wall-Mounted RF Sensors: Radio frequency sensors that detect falls and movements while preserving privacy. Non-invasive and provide constant surveillance.
“These advanced technologies enable healthcare professionals to respond quickly and effectively to potential falls, thereby improving patient outcomes and safety.”
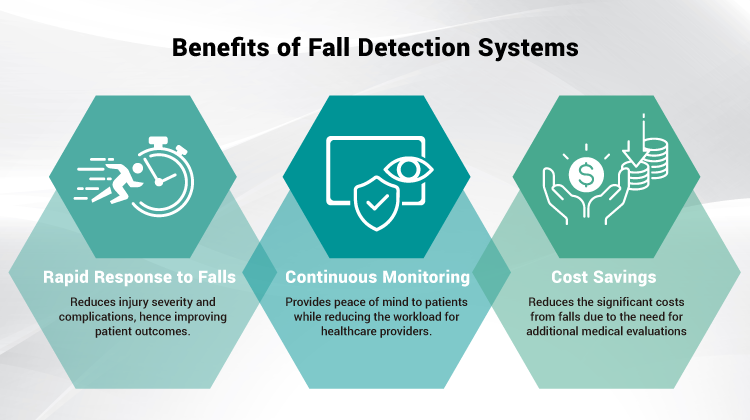
Benefits of Fall Detection Systems for Healthcare Setting
With a variety of fall detection technologies available, understanding their benefits is crucial for optimizing patient care. Implementing these systems in healthcare settings provides several key advantages:
Rapid Response to Falls
Fall detection systems alert healthcare staff immediately, reducing injury severity and complications such as fractures, lacerations, or internal bleeding. Swift intervention improves patient outcomes and recovery times.
Continuous Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is a key feature and benefit among various fall detection systems. It ensures constant patient observation, reducing unnoticed falls. This enhances safety by promptly detecting falls or unusual activities, providing peace of mind to patients and reducing the workload for healthcare providers.
Cost Savings
Hospitals incur significant costs from these falls due to the need for additional medical evaluations, treatments, and extended patient stays. The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) stopped reimbursing fall-related costs in 2008, making these events a financial burden for hospitals. A recent study in JAMA Health Forum found that the average cost of an inpatient fall is $62,521. Implementing fall detection systems helps avoid these expenses by preventing falls, resulting in substantial cost savings for healthcare facilities.
Limitations and Challenges
While fall detection systems offer numerous benefits, they also present certain limitations and challenges that must be addressed for optimal effectiveness.
Accuracy and Reliability
Fall detection systems' accuracy varies with sensor type, algorithm quality, and device placement. While some studies report high sensitivity and specificity rates, others find lower accuracy, particularly for slow or low falls, slumps, or crumples. False alarms can waste staff time and resources.
User Acceptance
Effective use requires widespread adoption by patients and staff. Concerns about wearing devices and data privacy need addressing. Systems must be user-friendly and unobtrusive to encourage acceptance.
Ongoing Evaluation
Continuous evaluation and refinement are essential for improving performance. Hospitals must be ready to update technologies as advancements occur.
Addressing these challenges through research and user-centered design is crucial for maximizing fall detection benefits in healthcare.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fall detection technologies offer significant advantages in improving patient safety and reducing healthcare costs. By understanding and addressing the limitations and challenges, healthcare facilities can effectively implement these systems to enhance patient care. Continuous evaluation and user-centered design will be essential in ensuring the success and effectiveness of fall detection technologies in the long run.
Reference
- Khan, S., Qamar, R., Zaheen, R., Al-Ali, A. R., Al Nabulsi, A., & Al-Nashash, H. (2018). Internet of things based multi-sensor patient fall detection system. Healthcare Technology Letters, 5(1), 41-46.
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. (2024). Preventing falls in hospitals.
- Mielenz, T. J., DiBardino, D., Phillips, S., Reddy, R., & Mixon, A. (2024). Cost-effectiveness of the Fall TIPS (Tailoring Interventions for Patient Safety) Program to prevent falls. JAMA Health Forum, 5(1), e2800748.